3.6.1 Depth Camera Usage Guide
Last Version: 11/09/2025
Overview
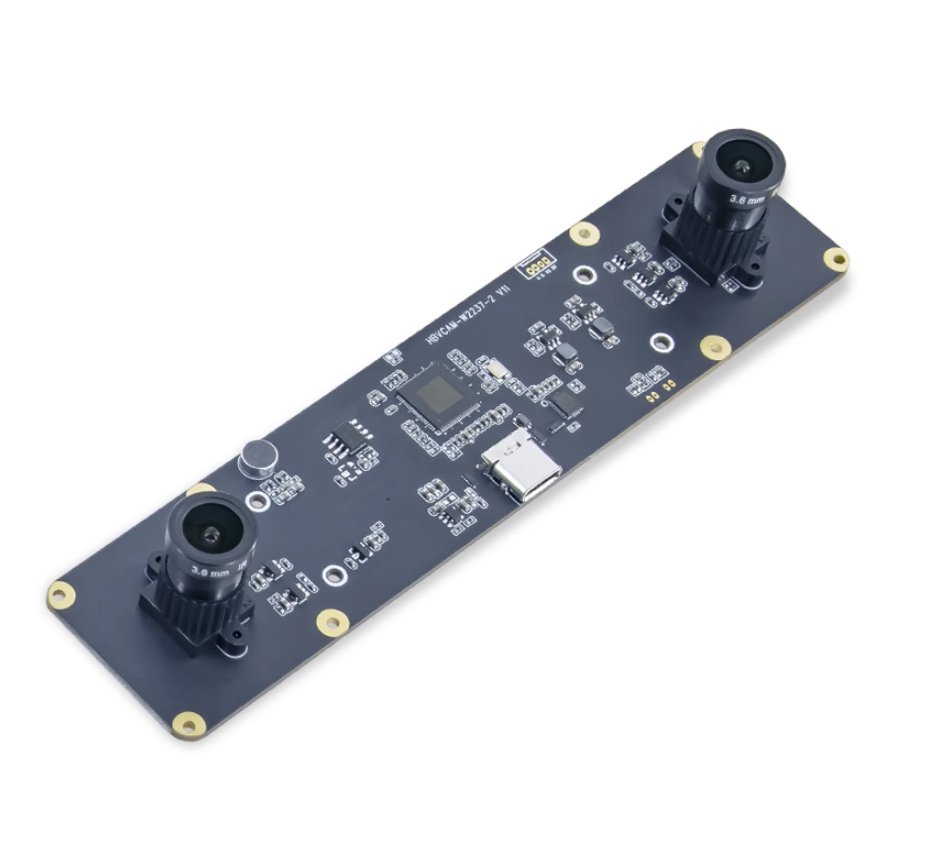
This guide provides instructions for using the HBV series stereo cameras, specifically the binocular, monochrome, global shutter, 720P models commonly available on the market.
Software Installation
Before using the camera, install GStreamer. Follow the official guide here: GStreamer User Guide
Usage Guide
Important: Always connect the camera to a USB 3.0 port for full performance.
Check Camera Device and Supported Formats
Run the following command to have the camera's supported resolutions and formats:
gst-device-monitor-1.0
Example output:
Device found:
name : USB Global Camera (V4L2)
class : Video/Source
caps : image/jpeg, width=2560, height=720, framerate={ (fraction)60/1, (fraction)60/1 }
image/jpeg, width=1600, height=600, framerate=100/1
image/jpeg, width=1280, height=480, framerate=100/1
image/jpeg, width=1280, height=400, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=1280, height=720, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=1280, height=712, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=800, height=600, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=800, height=592, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=640, height=480, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=640, height=472, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=640, height=400, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=640, height=392, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=640, height=240, framerate=100/1
image/jpeg, width=320, height=240, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=320, height=232, framerate=120/1
image/jpeg, width=2560, height=720, framerate={ (fraction)60/1, (fraction)60/1 }
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=2560, height=720, framerate={ (fraction)60/1, (fraction)60/1 }
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=1600, height=600, framerate=100/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=1280, height=480, framerate=100/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=1280, height=400, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=1280, height=720, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=1280, height=712, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=800, height=600, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=800, height=592, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=640, height=480, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=640, height=472, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=640, height=400, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=640, height=392, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=640, height=240, framerate=100/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=320, height=240, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=320, height=232, framerate=120/1
video/x-raw, format=YUY2, width=2560, height=720, framerate={ (fraction)60/1, (fraction)60/1 }
properties:
api.v4l2.cap.bus_info = usb-xhci-hcd.0.auto-1
api.v4l2.cap.capabilities = 84a00001
api.v4l2.cap.card = USB Global Camera: USB Global C
api.v4l2.cap.device-caps = 04200001
api.v4l2.cap.driver = uvcvideo
api.v4l2.cap.version = 6.6.63
api.v4l2.path = /dev/video20
device.api = v4l2
device.devids = 20785
device.id = 80
device.product.id = 0x155
device.vendor.id = 0x15a
factory.name = api.v4l2.source
media.class = Video/Source
node.description = USB Global Camera (V4L2)
node.name = v4l2_input.platform-xhci-hcd.0.auto-usb-0_1_1.0
node.nick = USB Global Camera
node.pause-on-idle = false
object.path = v4l2:/dev/video20
priority.session = 800
factory.id = 10
client.id = 35
clock.quantum-limit = 8192
media.role = Camera
node.driver = true
object.id = 81
object.serial = 90
gst-launch-1.0 pipewiresrc target-object=90 ! ...
Explanation:
- Top section (
caps): Lists supported resolutions and frame rates in bothimage/jpegandvideo/x-rawformats. - Bottom section (
properties): Shows detailed device properties. Note theapi.v4l2.pathvalue (e.g.,/dev/video20) as this device identifier will be used in subsequent commands.
Start the Camera
The camera supports two operation modes:
Mode 1: video/x-raw mode (no decoding, requires USB 3.0)
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video20 io-mode=2 ! "video/x-raw, width=2560, height=720, framerate=60/1" ! videoconvert ! waylandsink
Mode 2: image/jpeg mode (includes decoding, doesn't require USB 3.0)
# If the previous run was terminated with Ctrl+C, you may need to run this twice
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video20 io-mode=2 ! "image/jpeg, width=2560, height=720, framerate=60/1" ! spacemitdec ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! waylandsink
If you encounter errors like:
[MPP-ERROR] 11672:dequeueBuffer:495 Failed to dequeue buffer. type=9, memory=1
[MPP-ERROR] 11672:handleOutputBuffer:1431 dequeueBuffer failed, this dequeueBuffer must successed, because it is after Poll, please check! maybe after EOS?
Try running the command multiple times or reconnect the camera.
Save Video
video/x-raw mode:
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video20 io-mode=2 ! "video/x-raw, width=2560, height=720, framerate=60/1" ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! spacemith264enc ! filesink location=output.h264
image/jpeg mode:
gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video20 io-mode=2 ! "image/jpeg, width=2560, height=720, framerate=60/1" ! spacemitdec ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! spacemith264enc ! filesink location=output.h264
Use Camera with OpenCV
Important: OpenCV must be built with GStreamer support (WITH_GSTREAMER=ON).
#include <chrono>
#include <csignal>
#include <atomic>
#include <chrono>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
std::atomic<bool> running(true);
void signal_handler(int signum) {
std::cout << "\nCaught signal " << signum << ", exiting...\n";
running = false; // Set flag to exit while loop
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
signal(SIGINT, signal_handler); // Handle Ctrl-C
int video_idx = std::stoi(argv[1]);
std::string gst_pipeline = "v4l2src device=/dev/video" + std::to_string(video_idx) + " io-mode=2 ! " +
"video/x-raw,format=YUY2,width=2560,height=720,framerate=60/1 ! " +
"appsink";
cv::VideoCapture cap(gst_pipeline, cv::CAP_GSTREAMER);
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open camera" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
auto t0 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
cv::Mat frame;
int frame_id = 0;
while(running && cap.grab()){
cap.retrieve(frame);
frame_id += 1;
if(frame_id % 100 == 0){
auto t1 = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(t1 - t0).count();
printf("FPS %.2f Process \r\n", 100 / (duration / 1000000.0));
t0 = t1;
}
}
cap.release();
return 0;
}
Stereo Camera Calibration Process
-
Prepare Calibration Board
- Use this checkerboard generator.
- Set dimensions to 297x210mm (A4 paper standard) and print
- Recommended: more than 6×8 squares, square width > 25mm
-
Capture Calibration Images
- Capture images at specified resolution
- Use code to separate left/right images into respective folders (
leftandright) - Capture requirements:
- Both cameras must see the full checkerboard
- Capture from different distances and angles
- Avoid camera shake - capture when stable
- Avoid reflections on the calibration board
Python code for capturing calibration images:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("/dev/video0")# Use actual device number
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 1280)# Specify according to the required resolution.
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 480)# Specify according to the required resolution.
if os.path.exists("save"):
#directly remove the folder if it exists
os.system("rm -r save")
os.makedirs("save")
os.mkdir("save/left")
os.mkdir("save/right")
left_dir = "save/left"
right_dir = "save/right"
assert cap.isOpened(), "Cannot capture source"
cnt = 0
while True:
flag, frame = cap.read()
if not flag:
break
cv2.imshow("frame", frame)
left = frame[:, :frame.shape[1]//2]
right = frame[:, frame.shape[1]//2:]
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('q'):
break
if key == ord('s'):
cv2.imwrite(f"save/left/frame{cnt}.jpg", left)
cv2.imwrite(f"save/right/frame{cnt}.jpg", right)
cnt+=1
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows() -
MATLAB Calibration
Use the calibration tool in MATLAB to generate the calibration file. Example calibration screenshots:
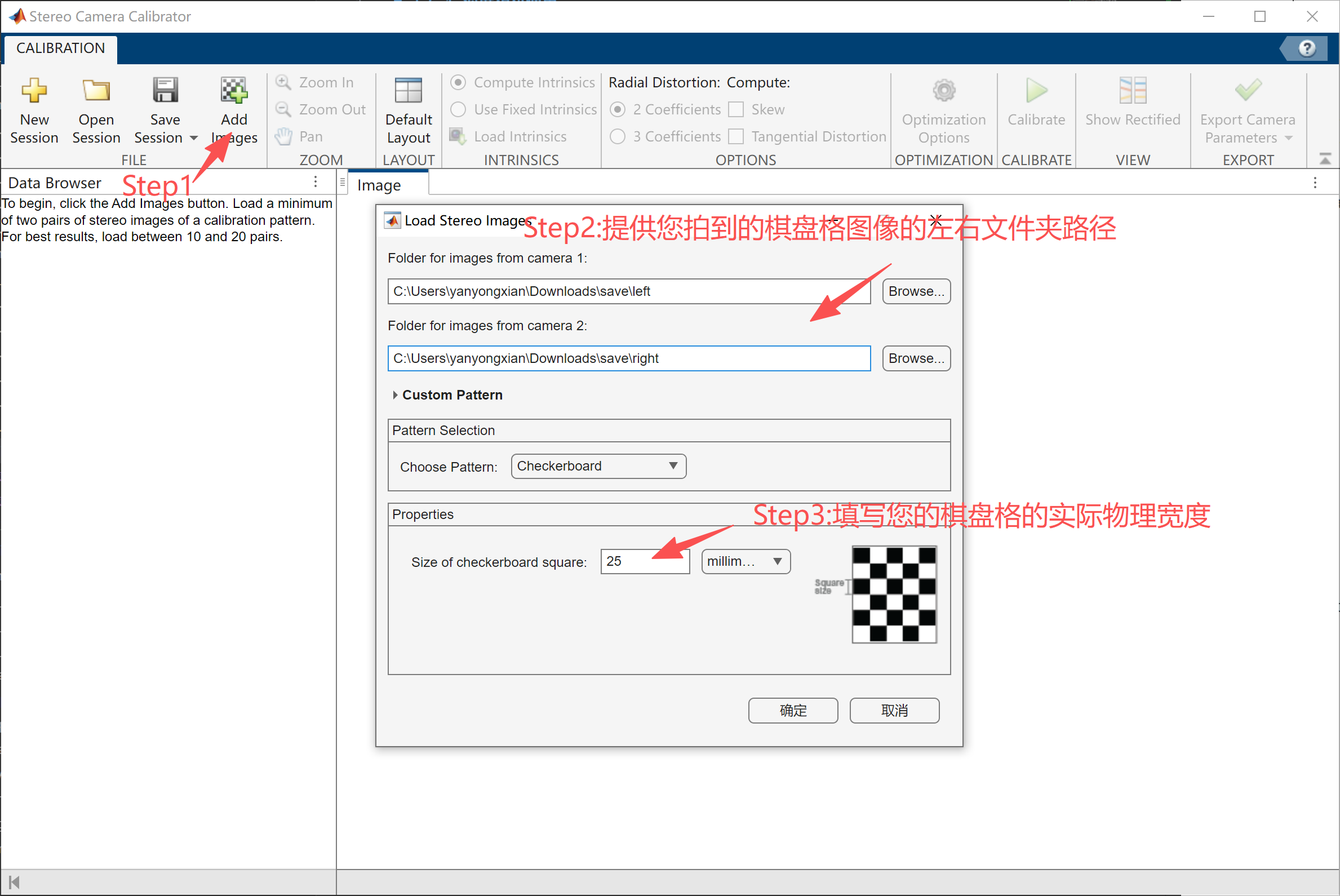
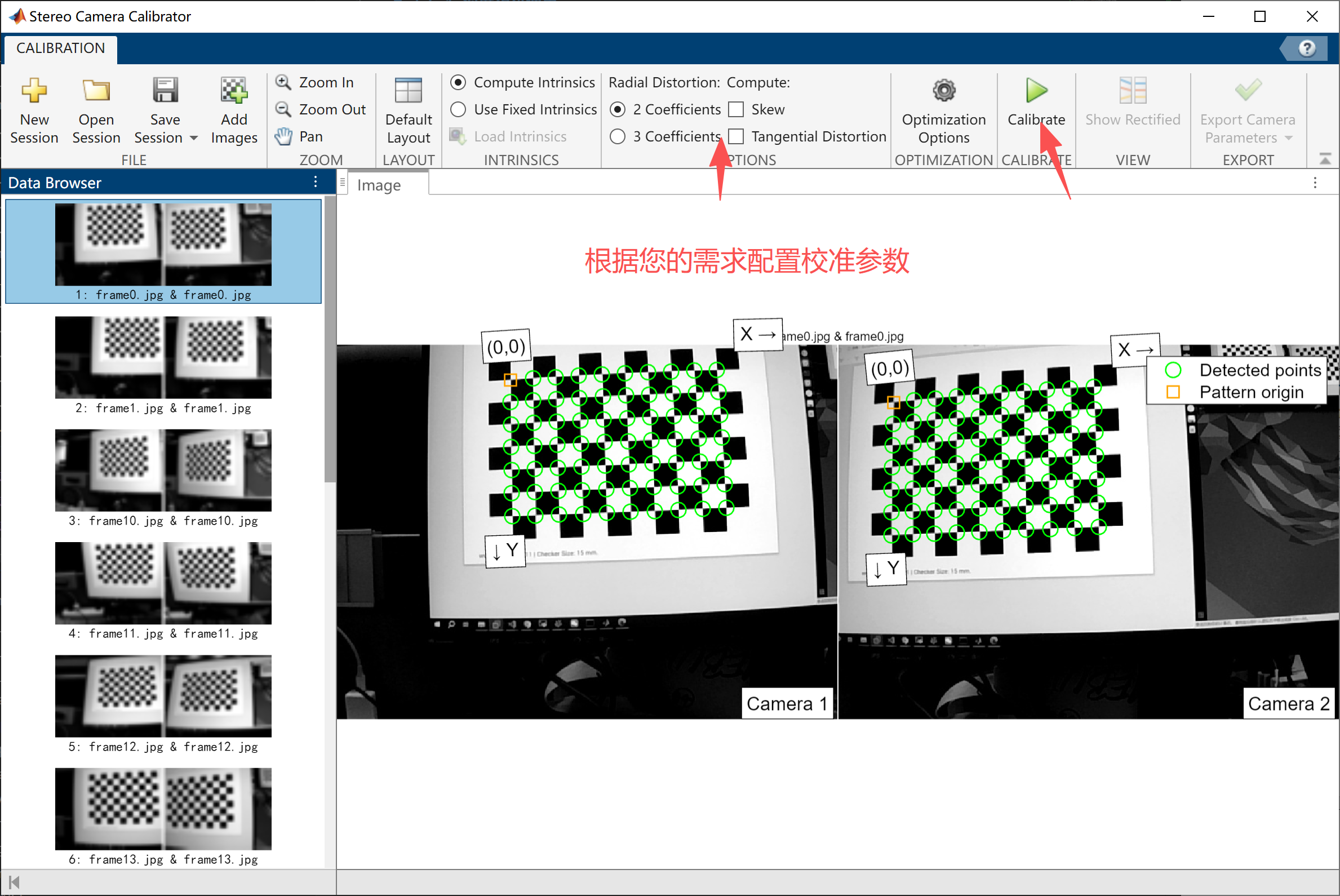
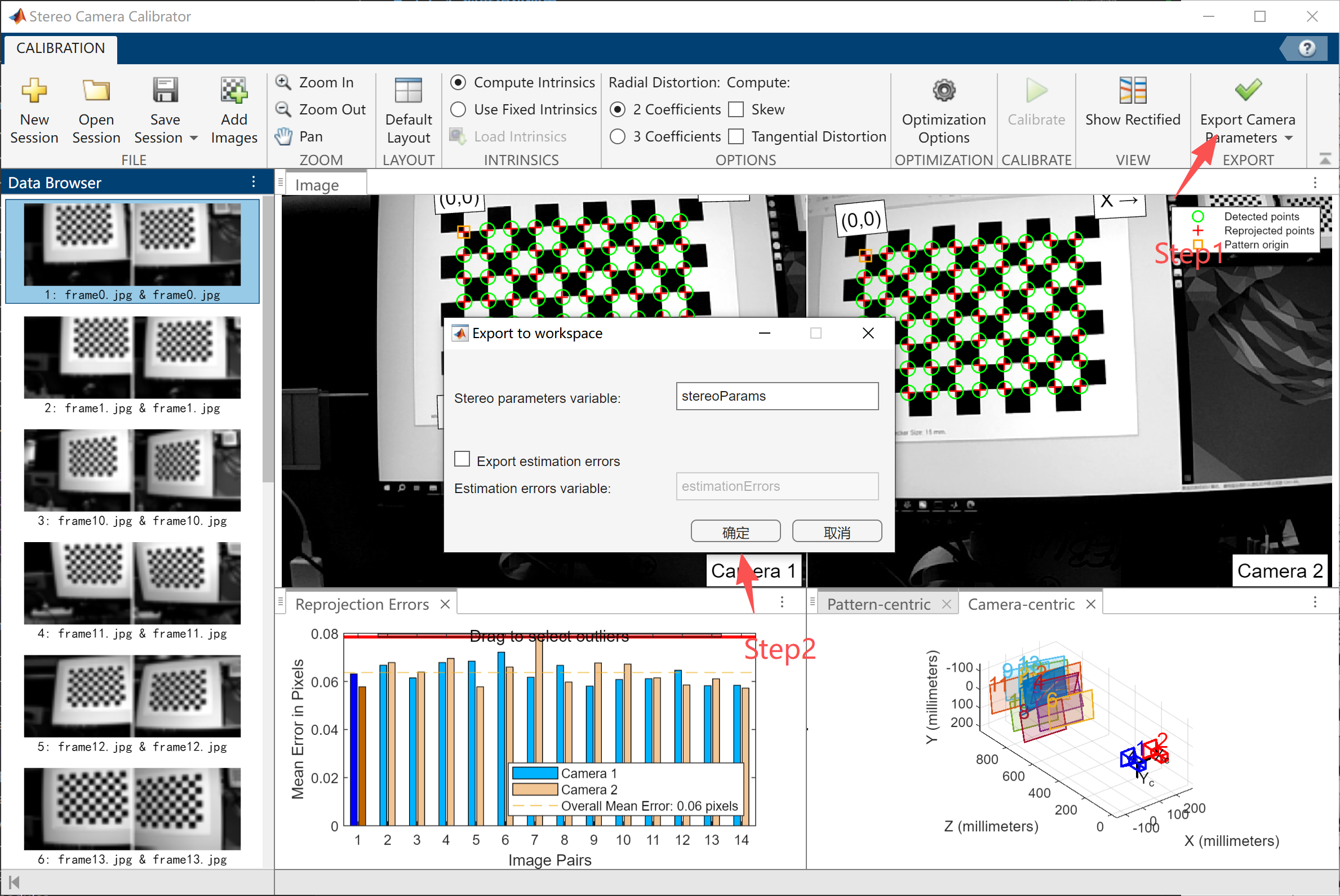
Important: The calibration error must be kept below 0.1.
-
Export Calibration File
% Extract camera intrinsic matrices
K1 = stereoParams.CameraParameters1.IntrinsicMatrix';
K2 = stereoParams.CameraParameters2.IntrinsicMatrix';
% Extract distortion coefficients from camera
D1 = stereoParams.CameraParameters1.RadialDistortion;
D1 = [D1, stereoParams.CameraParameters1.TangentialDistortion];
D2 = stereoParams.CameraParameters2.RadialDistortion;
D2 = [D2, stereoParams.CameraParameters2.TangentialDistortion];
% Extract rotation matrix and translation vector
R = stereoParams.RotationOfCamera2;
T = stereoParams.TranslationOfCamera2';
% Create YAML file content
yaml_content = sprintf('Camera1:\n');
yaml_content = [yaml_content, sprintf(' K: [%f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f] \n', K1(:))];
yaml_content = [yaml_content, sprintf(' D: [%f, %f, %f, %f] \n', D1)];
yaml_content = [yaml_content, sprintf('Camera2:\n')];
yaml_content = [yaml_content, sprintf(' K: [%f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f]\n', K2(:))];
yaml_content = [yaml_content, sprintf(' D: [%f, %f, %f, %f] \n\r', D2)];
yaml_content = [yaml_content, sprintf('R: [%f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f]\n', R(:))];
yaml_content = [yaml_content, sprintf('T: [%f, %f, %f] \n', T)];
% Save to file
fid = fopen('stereo_params.yaml', 'w');
fprintf(fid, yaml_content);
fclose(fid);
disp('YAML file generated: stereo_params.yaml');
-
Read Calibration File and Perform Stereo Matching in OpenCV
Install dependencies:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install libyaml-cpp-dev**C++ example code: **
#include <yaml-cpp/yaml.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <csignal>
#include <atomic>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
std::atomic<bool> running(true);
void signal_handler(int signum) {
std::cout << "\nCaught signal " << signum << ", exiting...\n";
running = false; //// Set the flag to exit the while loop
}
void readYaml(const std::string& filename, cv::Mat &K1, cv::Mat &D1, cv::Mat &K2, cv::Mat &D2, cv::Mat &R, cv::Mat &T) {
try {
YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile(filename);
// Read parameters for Camera1
std::vector<double> K1_vec = config["Camera1"]["K"].as<std::vector<double>>();
std::vector<double> D1_vec = config["Camera1"]["D"].as<std::vector<double>>();
// Read parameters for Camera2
std::vector<double> K2_vec = config["Camera2"]["K"].as<std::vector<double>>();
std::vector<double> D2_vec = config["Camera2"]["D"].as<std::vector<double>>();
// Read rotation matrix R and translation vector T
std::vector<double> R_vec = config["R"].as<std::vector<double>>();
std::vector<double> T_vec = config["T"].as<std::vector<double>>();
K1 = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_64F);
D1 = cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_64F);
K2 = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_64F);
D2 = cv::Mat(1, 4, CV_64F);
R = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_64F);
T = cv::Mat(3, 1, CV_64F);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
K1.at<double>(i / 3, i % 3) = K1_vec[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
D1.at<double>(0, i) = D1_vec[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
K2.at<double>(i / 3, i % 3) = K2_vec[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
D2.at<double>(0, i) = D2_vec[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
R.at<double>(i / 3, i % 3) = R_vec[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
T.at<double>(i, 0) = T_vec[i];
}
K1 = K1.t();
K2 = K2.t();
} catch (const YAML::Exception& e) {
std::cerr << "Error reading YAML file: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv){
signal(SIGINT, signal_handler);
cv::Mat K1, D1, K2, D2, R, T;
readYaml(argv[1], K1, D1, K2, D2, R, T);
std::cout << "K1: " << K1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "D1: " << D1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "K2: " << K2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "D2: " << D2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "R: " << R << std::endl;
std::cout << "T: " << T << std::endl;
T /= 1000.0; // Convert units (e.g., from mm to meters)
cv::Mat R1, R2, P1, P2, Q;
cv::stereoRectify(K1, D1, K2, D2, cv::Size(640, 480), R, T, R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, cv::CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY,0, cv::Size(640, 480));
cv::Mat map1x, map1y;
cv::initUndistortRectifyMap(K1, D1, R1, P1, cv::Size(640, 480), CV_16SC2, map1x, map1y);
cv::Mat map2x, map2y;
cv::initUndistortRectifyMap(K2, D2, R2, P2, cv::Size(640, 480), CV_16SC2, map2x, map2y);
cv::Ptr<cv::StereoSGBM> sgbm = cv::StereoSGBM::create(
0, 64, 1, 10, 150, 0, 3, 22, 3, 3, cv::StereoSGBM::MODE_SGBM_3WAY);
int video_idx = std::stoi(argv[2]);
std::string gst_pipeline = "v4l2src device=/dev/video" + std::to_string(video_idx) + " io-mode=2 ! " +
"video/x-raw,format=YUY2,width=1280,height=480,framerate=100/1 ! " +
"videoconvert ! " +
"video/x-raw, format=BGR ! " +
"appsink";
cv::VideoCapture cap(gst_pipeline, cv::CAP_GSTREAMER);
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
std::cerr << "Failed to open camera" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
auto save_vid = cv::VideoWriter("output.avi", cv::VideoWriter::fourcc('M', 'J', 'P', 'G'), 30, cv::Size(1280, 480));
while(running && cap.grab()){
cv::Mat frame;
cap.retrieve(frame);
cv::Mat left, right;
left = frame.colRange(0, frame.cols / 2).clone();
right = frame.colRange(frame.cols / 2, frame.cols).clone();
cv::remap(left, left, map1x, map1y, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
cv::remap(right, right, map2x, map2y, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
cv::Mat disp;
sgbm->compute(left, right, disp);
//disp = disp / 16.0 * 4
// disp.convertTo(disp, CV_16UC1);
cv::Mat disp_invalid;
disp_invalid = disp < 0;
disp.convertTo(disp, CV_8U, 1.0 / 4, 0);
cv::applyColorMap(disp, disp, cv::COLORMAP_JET);
disp.setTo(0, disp_invalid);
cv::Mat total;
cv::hconcat(left, disp, total);
save_vid.write(total);
}
save_vid.release();
cap.release();
return 0;
}
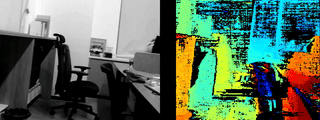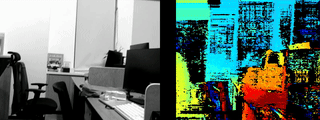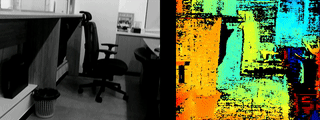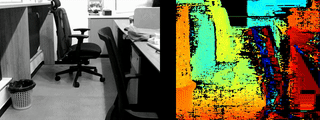
-
Result Example