3.3.3 PWM Usage Instructions
Last Version: 10/09/2025
This section explains how to use the gpiozero library together with the lgpio pin factory to generate PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals on the Bianbu Robot development platform. PWM is commonly used to control servos, adjust LED brightness, and regulate motor speed.
Environment Setup
Ensure that the gpiozero library is properly installed in your system or virtual environment:
pip install gpiozero
For environment setup and pin factory configuration, please refer to GPIO Usage Instructions.
PWM Pin Description
Before enabling PWM, consult Pin Definition Description to confirm which GPIO pins support hardware PWM.
- Hardware PWM pins are driven by SoC timers, offering better frequency stability and higher precision — ideal for timing-critical applications such as audio output or precise servo control.
- Software PWM can still be used on standard GPIO pins through
gpiozero, suitable for tasks with lower precision requirements.
Note: Ensure your chosen pins are not already used by other system services (e.g., audio, infrared). If there are conflicts, stop or disable the service before proceeding.
Example: Driving a Servo with PWM
This example outputs PWM signals on GPIO-70 to control the rotation angle of a standard servo.
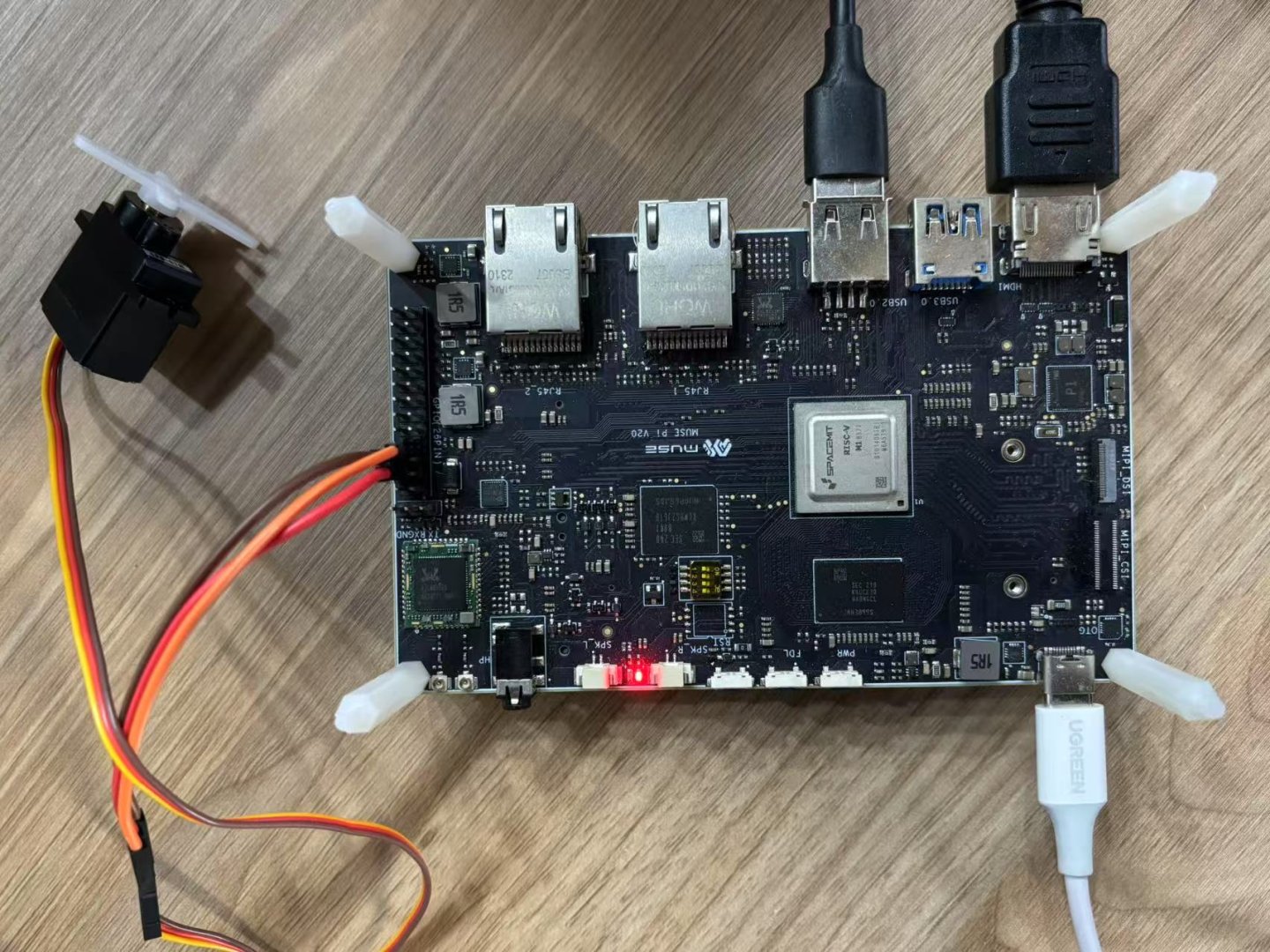
Physical Connection
| Servo Wire Color | Function | Connect to Board |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Power | 5V |
| Black | GND | GND |
| Yellow | Signal | GPIO-70 |
The connection diagram is shown below:
Test Code
# Configure LGPIO pin factory
from gpiozero.pins.lgpio import LGPIOFactory
from gpiozero import Device
Device.pin_factory = LGPIOFactory(chip=0)
# Import Servo control class
from gpiozero import Servo
from time import sleep
pin_number = 70 # PWM output pin
# Initialize Servo object with pulse width parameters
servo = Servo(
pin_number,
min_pulse_width=0.0005, # Minimum pulse width (seconds)
max_pulse_width=0.0025, # Maximum pulse width (seconds)
frame_width=0.02 # PWM period (seconds) = 20ms (50Hz)
)
# Control loop: adjust servo angle via user input
while True:
user_input = input("Enter a float between -1 and 1 (to control angle): ")
try:
value = float(user_input)
if -1 <= value <= 1:
servo.value = value
sleep(0.3)
servo.detach() # Stop signal output to prevent servo jitter
else:
print("Input out of range, please enter a value between -1 and 1.")
except ValueError:
print("Invalid input, please enter a valid float number.")
Control Notes:
- Input
-1→ Servo moves to minimum angle (~0°) - Input
0→ Servo moves to center position (~90°) - Input
1→ Servo moves to maximum angle (~180°)