3.3.5 SPI Usage Instructions
Last Version: 2025/09/26
This guide explains how to configure and use the SPI interface on the development board.
Overview
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is a serial communication interface commonly used between SoCs and peripherals. It supports single-lane (x1) mode only on this platform.
SPI operates in two modes: Master and Slave, typically with one master device controlling one or more slave devices.
Note: On K1, SPI currently supports master mode only.
Pin Functions
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| SCLK (Serial Clock) | Clock signal |
| MISO (Master In Slave Out) | Data from slave to master |
| MOSI (Master Out Slave In) | Data from master to slave |
| CS/SS (Chip Select / Slave Select) | Slave device selection |
Pin Reference
Refer to the Pin Definition Description for available SPI pins on your board.
For example, on MUSE-Pi-Pro, supported SPI pins are shown below:
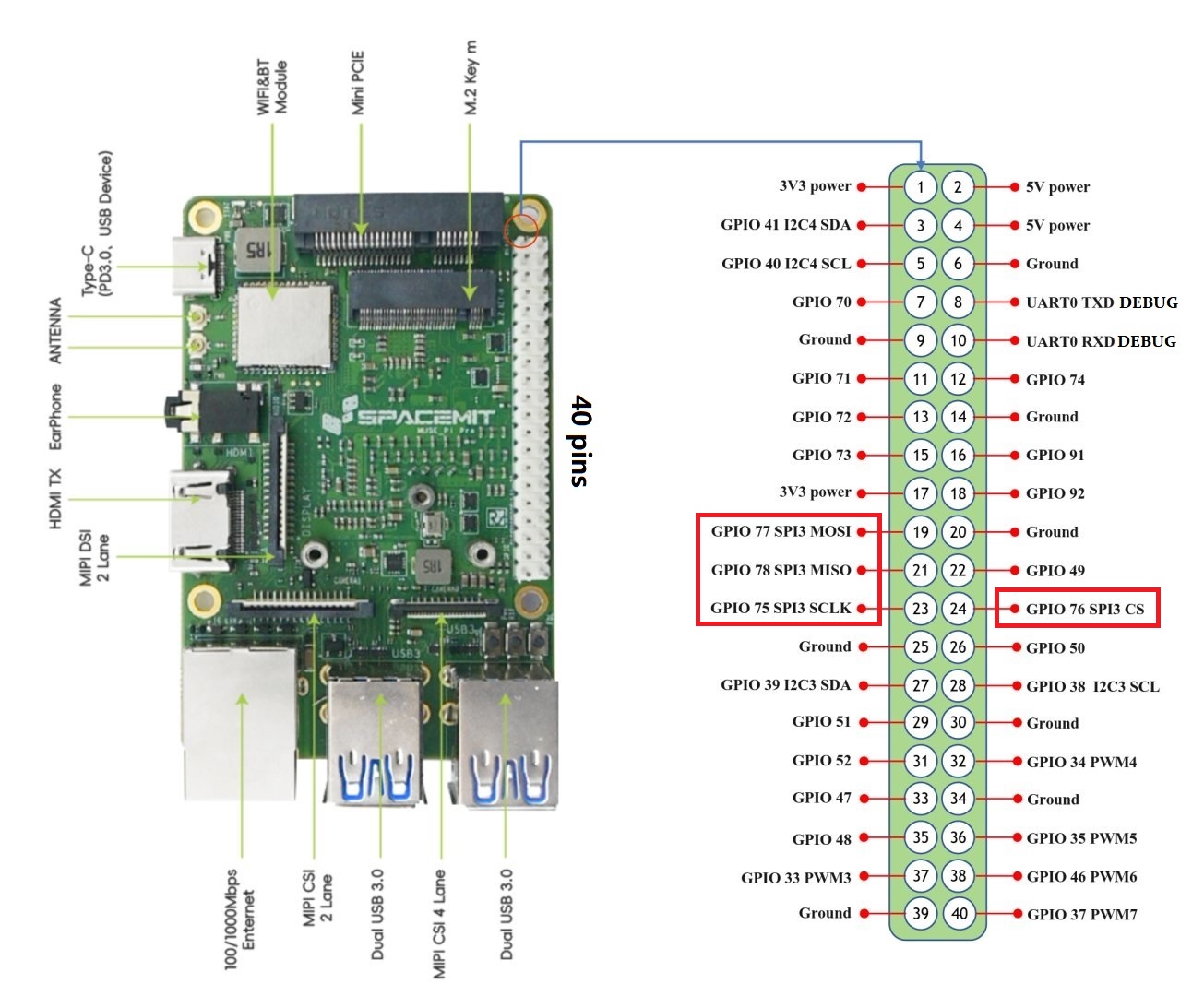
Checking Device Information
-
List SPI bus devices and driver info
ls /sys/bus/spiExample output:
spi--
|-- devices //SPI 总线上的设备
|-- drivers //SPI 总线上注册的设备驱动
|-- drivers_autoprobe
|-- drivers_probe -
Inspect a specific SPI device:
ls -la /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi3.0 -
Check the device modalias (driver name):
cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi3.0/modalias -
Check the device maximum frequency:
cat /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi3.0/of_node/spi-max-frequency
Enabling SPI
SPI pins (GPIO75, 76, 77, 78) are multiplexed with other functions. Before using SPI, you must disable any conflicting devices in the device tree (DTS).
Two approaches are available (choose one):
- Method A: Download and install a pre-built DTB file
- Method B: Manually edit and recompile the DTS
Method A: Download Pre-compiled DTB File
-
Download a preconfigured DTB file:
wget https://archive.spacemit.com/ros2/prebuilt/brdk_libs/spi/k1-x_MUSE-Pi-Pro.dtb -
Save it to
/boot/spacemit/6.6.63/, replacing the existing DTB.
Method B: Manual DTS Modification and Compilation
-
Extract the DTS from the current DTB
cd /boot/spacemit/6.6.63/ // DTS location
sudo apt update
sudo apt install device-tree-compiler // Compiler installation
sudo dtc -I dtb -O dts -o k1-x_MUSE-Pi-Pro.dts k1-x_MUSE-Pi-Pro.dtb // Decompile DTB to DTS
ls
// Verify successful decompilation with k1-x_MUSE-Pi-Pro.dts -
Modify Device Tree Edit
k1-x_MUSE-Pi-Pro.dtsand modify these two SPI nodes:-
Modify spi@d420c000 node:
- Disable original node and flash subnode: set
status = "disabled" - Add spi@3 subnode
- Disable original node and flash subnode: set
-
Modify spi@d401c000 node:
- Add spi@3 subnode
Specific modifications as below:
// Modify spi@d420c000 node
spi@d420c000 {
compatible = "spacemit,k1x-qspi";
#address-cells = <0x01>;
#size-cells = <0x00>;
reg = <0x00 0xd420c000 0x00 0x1000 0x00 0xb8000000 0x00 0xc00000>;
reg-names = "qspi-base\0qspi-mmap";
k1x,qspi-sfa1ad = <0x4000000>;
k1x,qspi-sfa2ad = <0x100000>;
k1x,qspi-sfb1ad = <0x100000>;
k1x,qspi-sfb2ad = <0x100000>;
clocks = <0x03 0x8f 0x03 0x90>;
clock-names = "qspi_clk\0qspi_bus_clk";
resets = <0x1d 0x4e 0x1d 0x4f>;
reset-names = "qspi_reset\0qspi_bus_reset";
k1x,qspi-pmuap-reg = <0xd4282860>;
k1x,qspi-mpmu-acgr-reg = <0xd4051024>;
k1x,qspi-freq = <0x1945ba0>;
k1x,qspi-id = <0x04>;
power-domains = <0x20 0x00>;
cpuidle,pm-runtime,sleep;
interrupts = <0x75>;
interrupt-parent = <0x1e>;
k1x,qspi-tx-dma = <0x01>;
k1x,qspi-rx-dma = <0x01>;
dmas = <0x21 0x2d 0x01>;
dma-names = "tx-dma";
interconnects = <0x22>;
interconnect-names = "dma-mem";
status = "disabled"; // Disable this node
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0x5b>;
flash@0 {
compatible = "jedec,spi-nor";
reg = <0x00>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x1945ba0>;
m25p,fast-read;
broken-flash-reset;
status = "disabled"; // Disable flash subnode
};
// Add spi@3 subnode
spi@3 {
compatible = "cisco,spi-petra";
reg = <0x0>;
spi-max-frequency = <6400000>;
status = "okay";
};
};// Modify spi@d401c000 node
spi@d401c000 {
compatible = "spacemit,k1x-spi";
reg = <0x00 0xd401c000 0x00 0x34>;
k1x,ssp-id = <0x03>;
k1x,ssp-clock-rate = <0x186a000>;
dmas = <0x21 0x14 0x01 0x21 0x13 0x01>;
dma-names = "rx\0tx";
power-domains = <0x20 0x00>;
cpuidle,pm-runtime,sleep;
interrupt-parent = <0x1e>;
interrupts = <0x37>;
clocks = <0x03 0x58>;
resets = <0x1d 0x18>;
#address-cells = <0x01>;
#size-cells = <0x00>;
interconnects = <0x22>;
interconnect-names = "dma-mem";
status = "okay";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <0x2e>;
k1x,ssp-disable-dma;
// Add spi@3 subnode
spi@3 {
compatible = "cisco,spi-petra";
reg = <0x0>;
spi-max-frequency = <6400000>;
status = "okay";
};
}; -
-
Compile New Device Tree
sudo dtc -I dts -O dtb -o k1-x_MUSE-Pi-Pro.dtb k1-x_MUSE-Pi-Pro.dts -
Update Kernel Image
wget https://archive.spacemit.com/ros2/prebuilt/brdk_libs/spi/vmlinuz-6.6.63
// Copy to /boot/ directory, replacing old vmlinuz-6.6.63 image -
Reboot Development Board
sudo rebootAfter reboot, the device should appear as
/dev/spi3.0.
Usage Example
-
Wiring master and slave devices
Connect as below:
Master Device <===> Slave Device
SCK --------------> SCK
MOSI --------------> MOSI (or SDI)
MISO <-------------- MISO (or SDO)
CS0 --------------> CS (or nSS) -
List available SPI devices
ls /dev/spi*
# Expected output: spi3 -
SPI Master Example Code
//spi_master.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define SPI_DEV "/dev/spidev3.0"
#define BUF_SIZE 32
static uint32_t mode = SPI_MODE_0;
static uint8_t bits = 8;
static uint32_t speed = 1000000;
int spi_init()
{
int fd = open(SPI_DEV, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("Failed to open SPI device");
return -1;
}
if (ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MODE, &mode) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set SPI mode");
goto error;
}
if (ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set word length");
goto error;
}
if (ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed) < 0) {
perror("Failed to set SPI speed");
goto error;
}
return fd;
error:
close(fd);
return -1;
}
int spi_transfer(int fd, uint8_t *tx_buf, uint8_t *rx_buf, int len)
{
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr =
{
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx_buf,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx_buf,
.len = len,
.speed_hz = speed,
.bits_per_word = bits,
.delay_usecs = 0,
};
if (ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr) < 1) {
perror("SPI transfer failed");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int fd = spi_init();
if (fd < 0) return 1;
uint8_t tx_buf[BUF_SIZE] = {0};
uint8_t rx_buf[BUF_SIZE] = {0};
tx_buf[0] = 0x9f;
spi_transfer(fd, tx_buf, rx_buf, strlen((char *)tx_buf) + 3);
printf("Slave response: %x%x%x%x\n", rx_buf[0], rx_buf[1], rx_buf[2], rx_buf[3]);
while (1)
{
printf("Master> ");
fgets((char *)tx_buf, BUF_SIZE, stdin);
if (strncmp((char *)tx_buf, "quit", 4) == 0) break;
if (spi_transfer(fd, tx_buf, rx_buf, strlen((char *)tx_buf) + 3) == 0) {
printf("Slave response: %x%x%x%x\n", rx_buf[0], rx_buf[1], rx_buf[2], rx_buf[3]);
}
memset(tx_buf, 0, BUF_SIZE);
memset(rx_buf, 0, BUF_SIZE);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
-
Cross-compile on the host:
riscv64-unknown-linux-gnu-gcc -O2 -mcpu=spacemit-x60 -march=rv64gc_zba_zbb_zbc_zbs spi_master.c -o spi_masterFor tool installation and usage, please refer to Cross-Compilation Toolchain
-
Copy executable to board:
scp spi_master bianbu@10.0.91.35:/home/bianbuDescription:
-
scp- SSH remote secure copy command -
spi_master- Executable filename -
bianbu- Development board username -
10.0.91.35- Board IP address (check withhostname -I) -
/home/bianbu- Destination directory
Note: Ensure host and development board are on the same network.
-
-
Run on development board:
sudo ./spi_masterExpected output:
Slave response: 0000
Master> 9f
Slave response: 0000