1.4 Remote Access
This guide explains how to remotely connect to your Bianbu ROS board from a PC using Serial, SSH, or VNC. It includes connection methods, step-by-step instructions, and tool setup.
Serial Port Login
Serial port access is useful for debugging, monitoring firmware flashing, or working without a network connection.
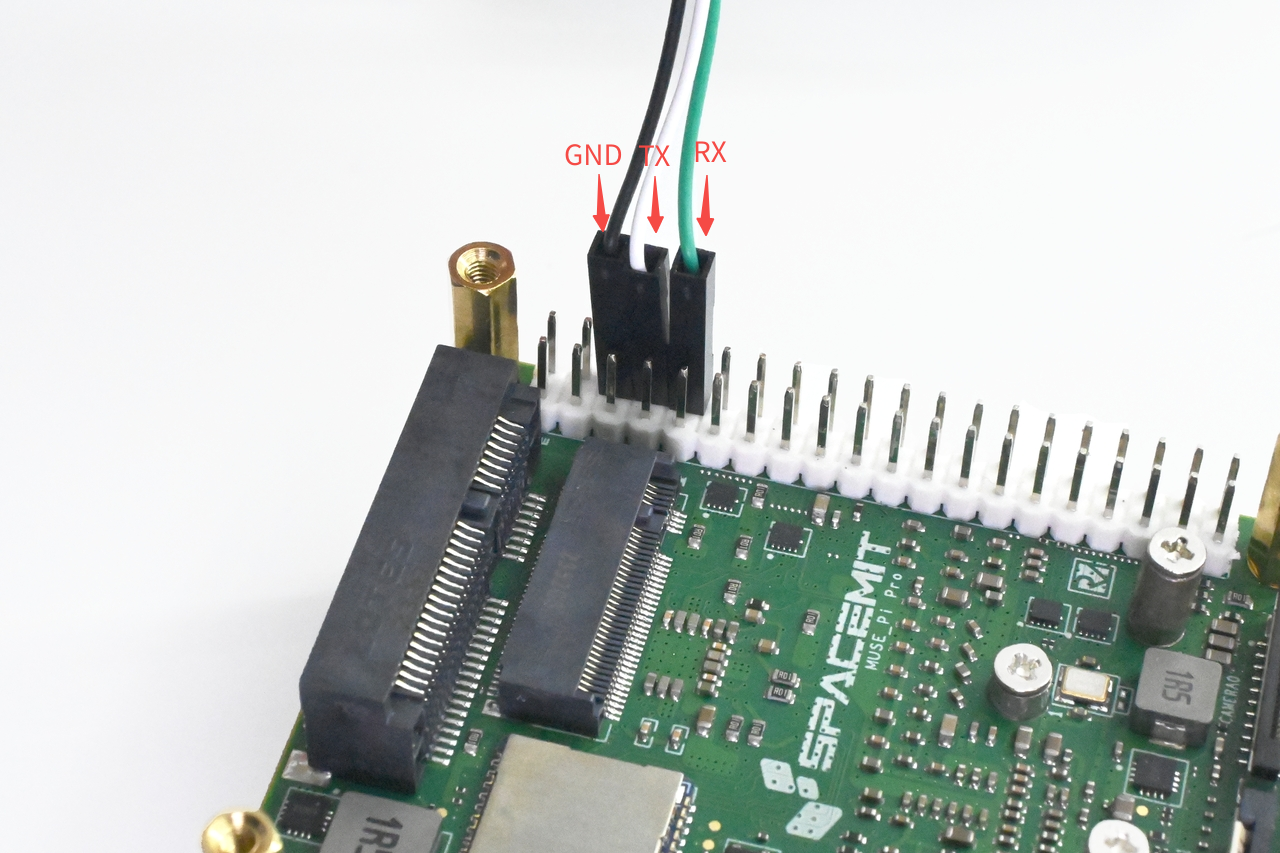
Hardware Connection
Connect your PC to the MUSE Pi Pro board using a USB-to-TTL adapter. Attach the GND, TX, and RX pins as shown:

Login on Windows (using MobaXterm)
Using MobaXterm as an example:
-
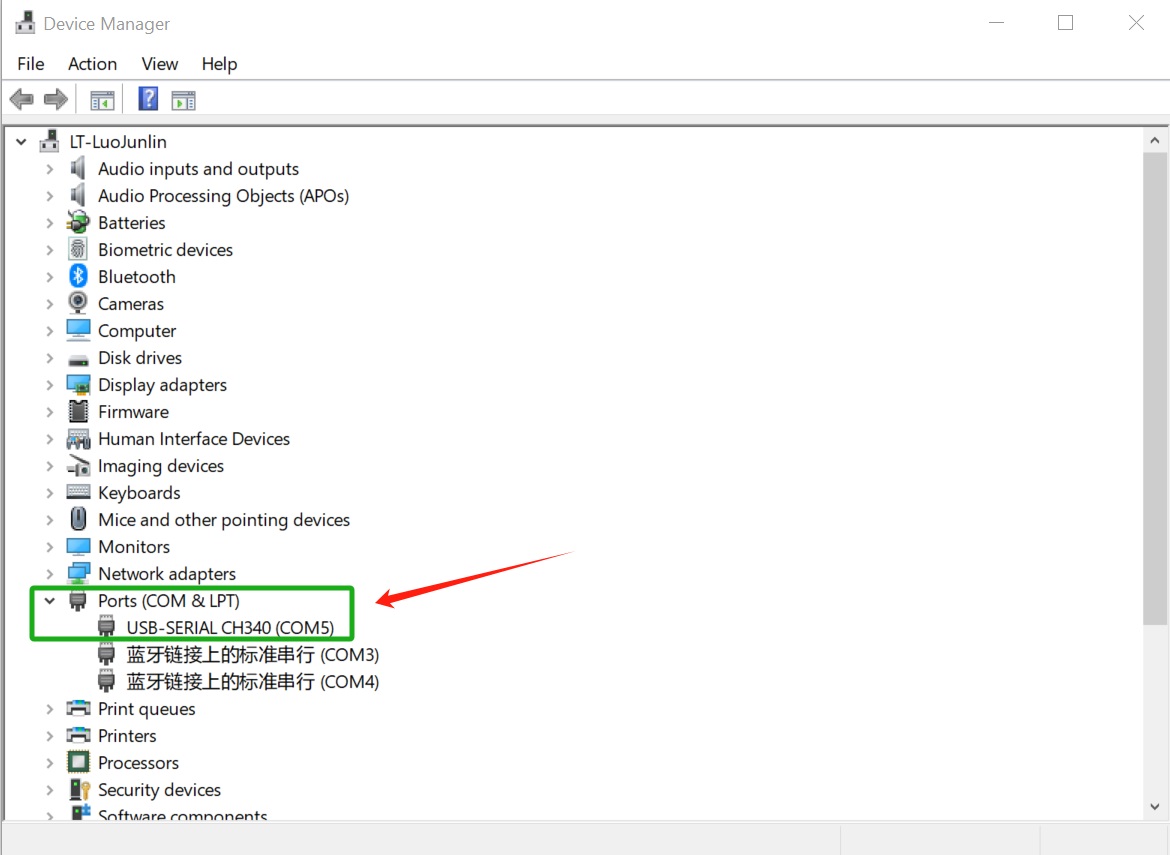
Connect the serial adapter and check Device Manager to find the COM port (e.g., COM5).
-
Open MobaXterm → Sessions → New Session, then select Serial.
-
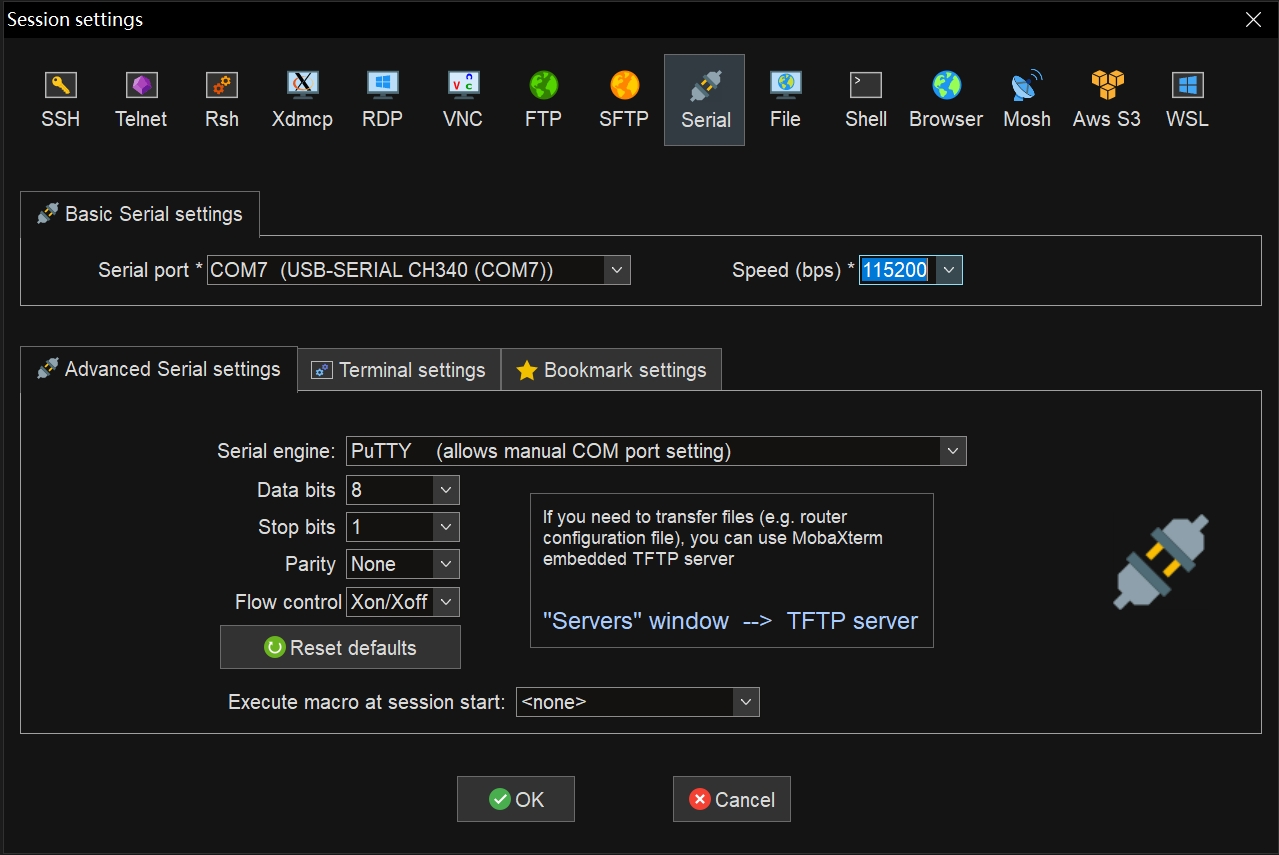
In the configuration Session:
- Serial port: Select the detected COM port (e.g., COM5)
- Speed: Set to 115200
- Click OK to open the terminal session.
Login on Ubuntu
-
Check the available serial devices:
ls -al /dev/ttyUSB* -
If the device is
/dev/ttyUSB0, connect using the toolminicom:sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyUSB0If
minicomis not installed, run:sudo apt install minicomFor first-time setup on
minicom, configure the baud rate:sudo minicom -sSet Serial port speed to
115200and save the configuration.
💡 Tip: If login fails or get a permission error, add your user to the
dialoutgroup:sudo usermod -aG dialout $USER
SSH Login
SSH is a common way to access the development board remotely over a local network.
Note: Ensure the board is connected to the network. For instructions, see Section Network Setup.
Connecting from (using MobaXterm)
Using MobaXterm as recommended:
-
Open MobaXterm → Sessions → New Session, then select SSH.
-
Configure SSH Settings:
- Remote host: Enter the board’s IP address (e.g.,
192.168.1.100) - Specify username: Keep default
bianbu - Port: Keep default
22
- Remote host: Enter the board’s IP address (e.g.,
-
Click OK, then enter the password to log in.
Connecting from Ubuntu
Open a terminal and run:
ssh bianbu@<remote_ip>
Replace <remote_ip> with the board’s IP address.
On first login, confirm the fingerprint by typing yes.
VNC Login
VNC provides remote graphical desktop access and requires the VNC service to be running on the development board.
For enabling VNC, see: 1.3 Enable VNC Service.
Connecting from Windows
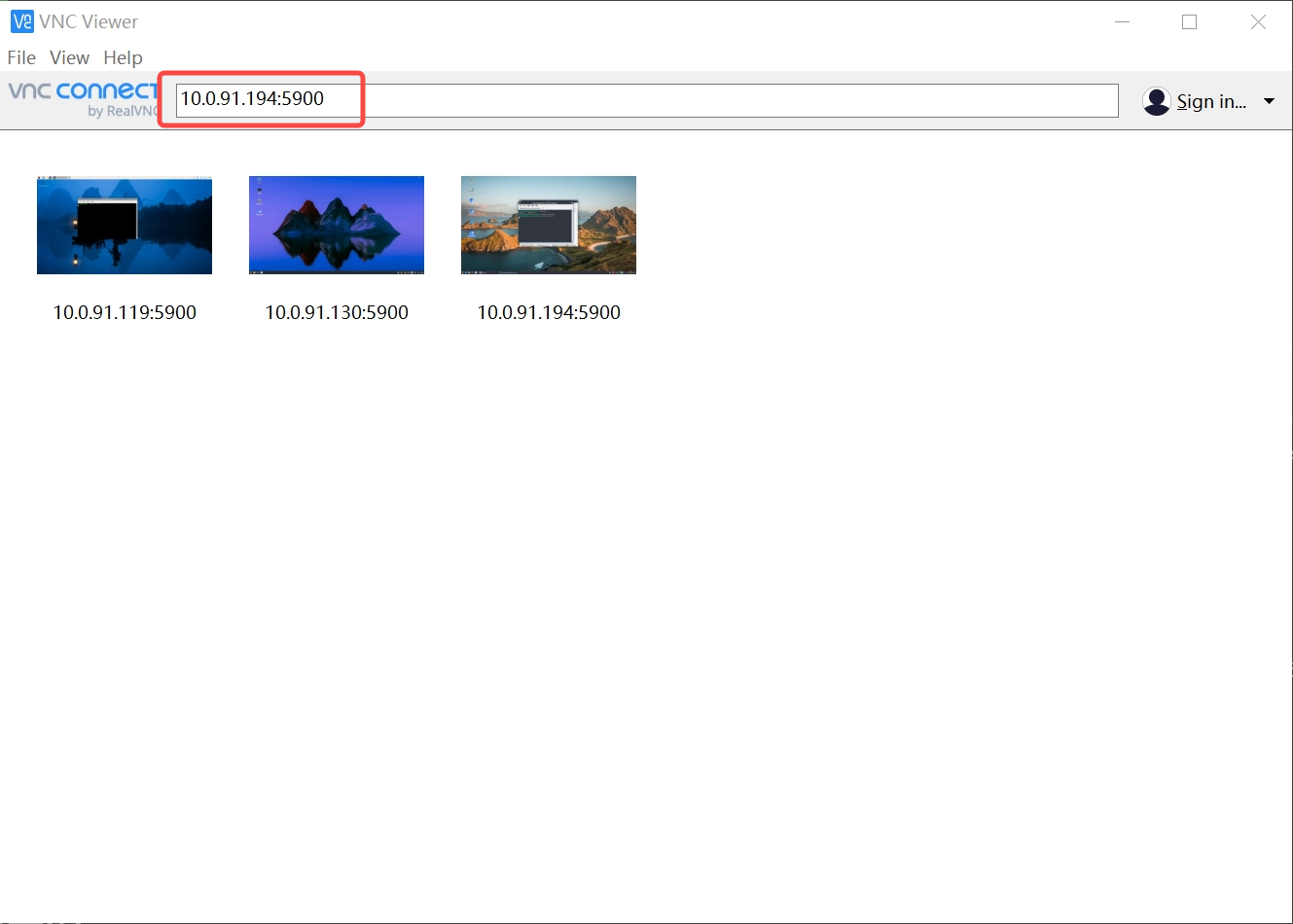
Using RealVNC Viewer as recommended:
- Launch VNC Viewer.
- Enter the address
<remote_ip>:5900(e.g.,192.168.1.100:5900) in the address bar. - Press Enter to connect.
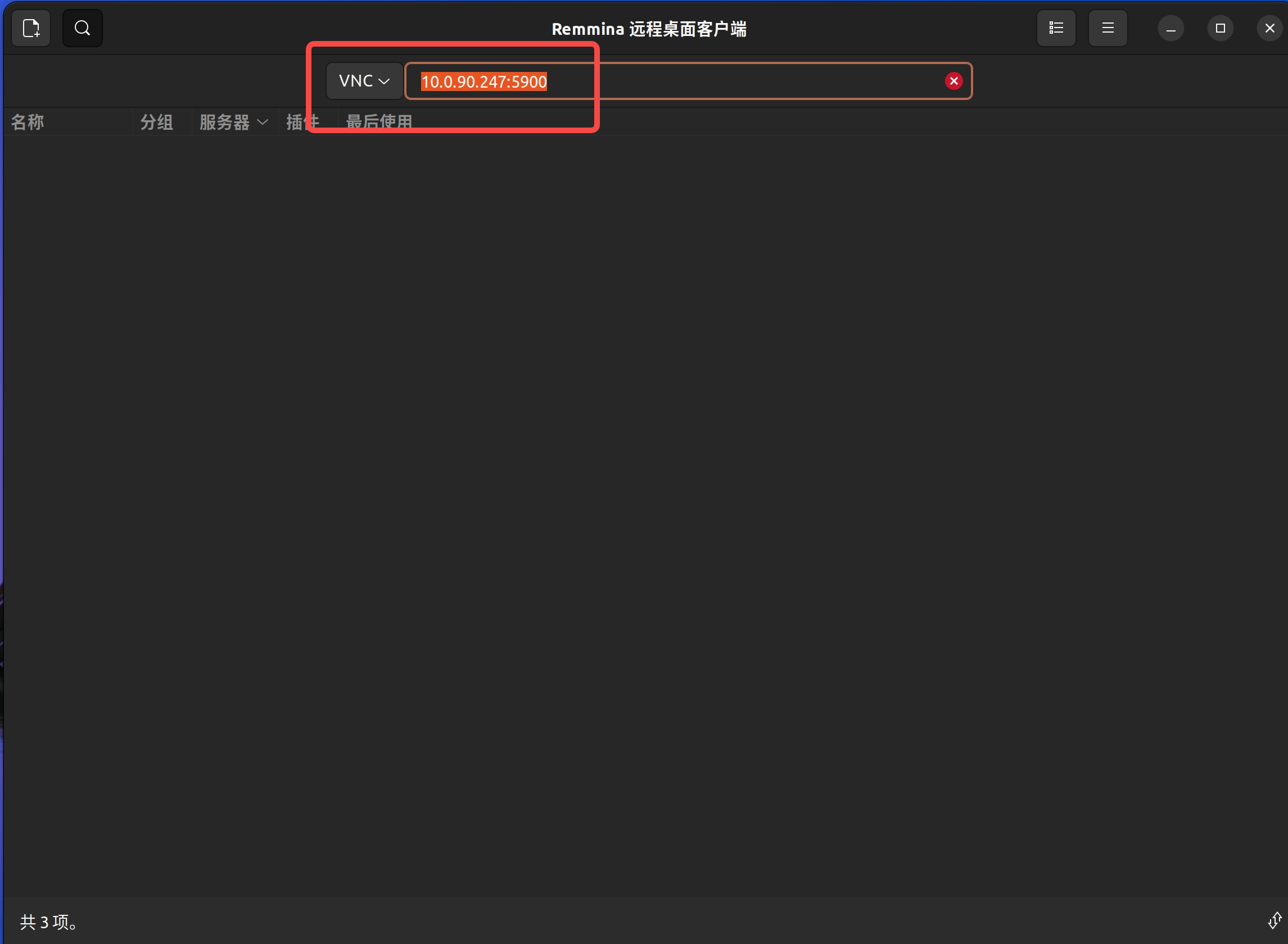
Connecting from Ubuntu
Using Remmina as recommended:
-
Install Remmina:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install remmina remmina-plugin-rdp remmina-plugin-vnc remmina-plugin-secret -
Launch Remmina:
remmina -
Configure connection:
- Select VNC as the protocol
- Enter
<remote_ip>:5900(e.g.,192.168.1.100:5900) in the address bar. - Press Enter to connect