Node-RED Usage Guide
Last Version: 2025/09/25
This guide shows how to run Node-RED inside Docker on the Bianbu system.
Introduction
Node-RED is a flow-based, visual programming tool originally created by IBM engineers and now maintained by the open-source community (with support from the JS Foundation).
It is mainly used for
- event-driven application integration
- IoT (Internet of Things) development
- API orchestration
- Automation
✨ Key Features
-
Low-code / Visual Programming
- Build logic by dragging and dropping nodes and connecting them with wires.
- Minimal coding required to create powerful flows.
-
Built on Node.js
- Runs on top of Node.js.
- Lightweight, suitable for embedded devices and cloud platforms.
-
Built-in and Extendable Nodes
- Includes numerous pre-built nodes: HTTP, MQTT, WebSocket, file system, function processing, etc.
- Extend functionality via npm with community-contributed nodes (databases, AI services, chatbots, Slack, Telegram, robotics, and more).
-
Designed for IoT
- Easy integration with sensors, devices, and cloud services using MQTT, REST APIs, or Modbus protocol.
- Popular for smart home and industrial IoT projects.
-
Highly Extensible
- Add custom logic with JavaScript function nodes.
- Integrate with databases (MongoDB, MySQL, Redis), messaging systems (Kafka, RabbitMQ), and AI services (TensorFlow.js, OpenAI API).
Pull the Image
Run the following command to download the latest Node-RED Docker image:
sudo docker pull harbor.spacemit.com/bianbu-robot/node-red-image:latest
Start Node-RED
Launch the Node-RED service with:
sudo docker run -it \
-p 1880:1880 \
-v node_red_data:/data \
--name node-red-test \
harbor.spacemit.com/bianbu-robot/node-red-image:latest
Command breakdown
docker runRuns a container. If the image isn’t available locally, it will be downloaded first.-itOpens an interactive terminal so you can see the container’s output in real time.-p 1880:1880Maps port1880on your local machine to port1880inside the container.-v node_red_data:/dataMounts a Docker volume namednode_red_datato the container’s/datadirectory. This ensures your flow changes are saved. You can also use a local path instead ofnode_red_data.--name node-red-testGives the container a recognizable name.harbor.spacemit.com/bianbu-robot/node-red-image:latestSpecifies the base image to use.
Terminal output example:
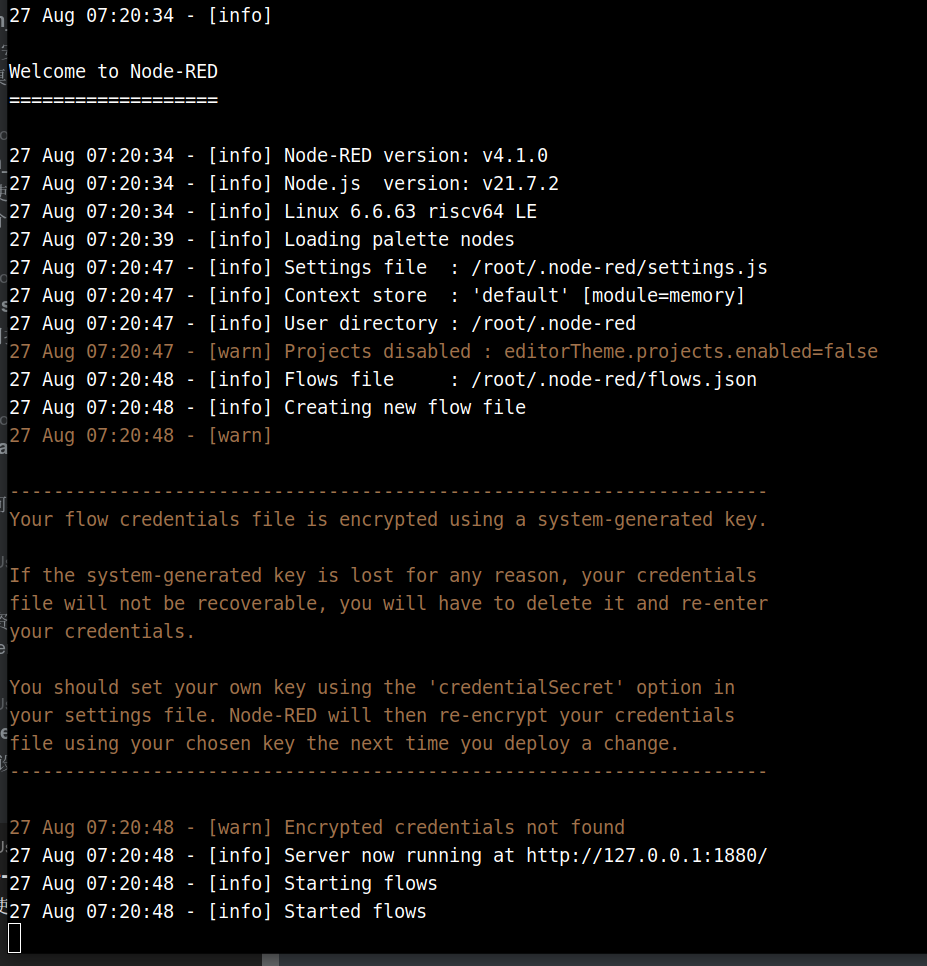
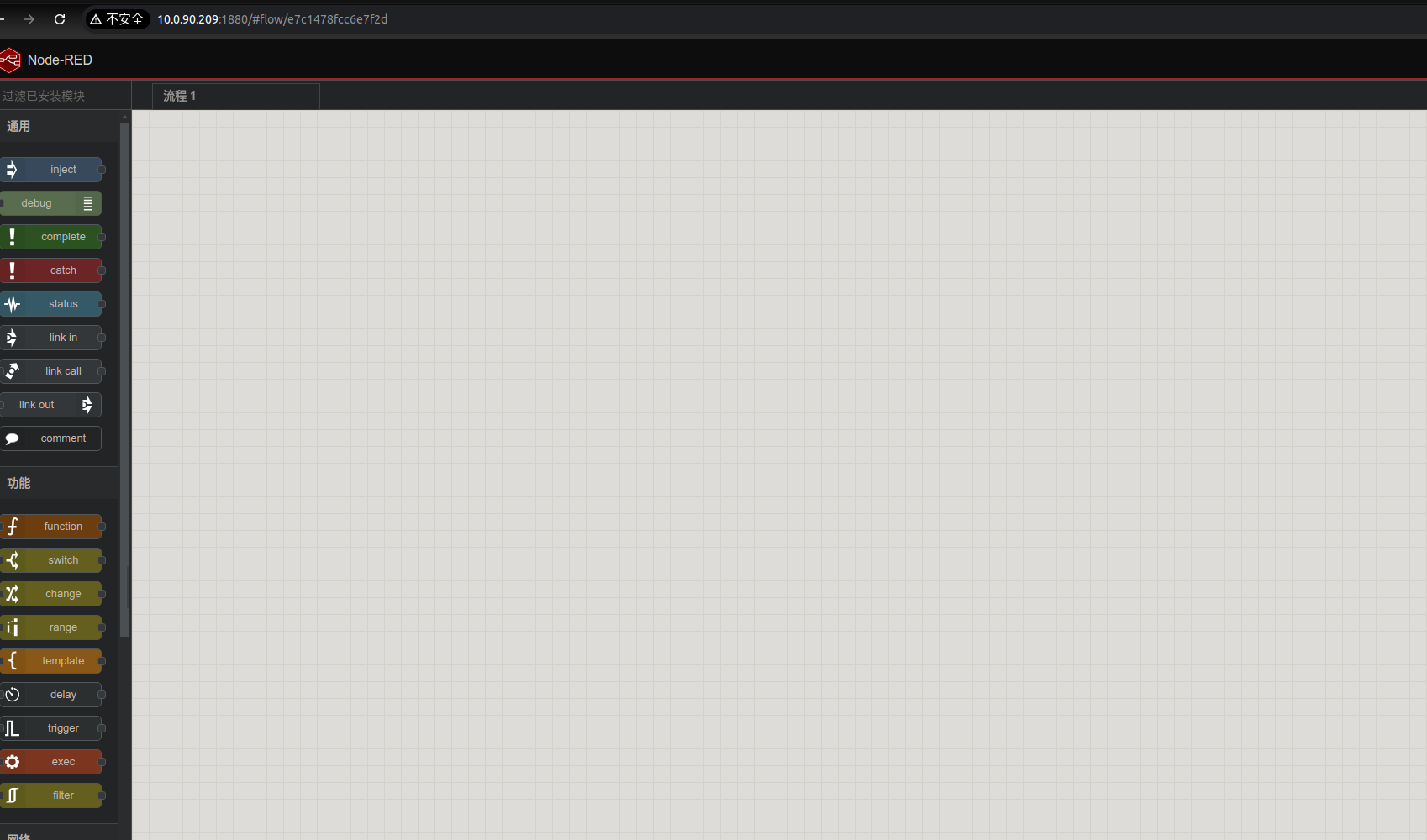
Access the Node-RED Dashboard
Open a browser on your x86 PC and visit http://board_ip:1880/
Note: Replace board_ip with your development board’s actual IP address.
The interface will look like this:
Manage the Container
-
Run in background To detach from the container but keep it running, press Ctrl+p then Ctrl+q.
-
To reattach to the terminal and view logs:
docker attach node-red-test -
To restart the container (e.g., after a system or Docker service restart):
docker start node-red-test -
To stop the container:
docker stop node-red-test
Learn More
You can now follow the Official Tutorial to build more flows.