6.4.4 SLAM
Last Version: 12/09/2025
Overview
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) is a technique that builds a map of the environment in real time using sensor data, while simultaneously estimating the robot’s position and orientation. This provides the perception information needed for robot navigation.
This example demonstrates SLAM in both simulation and real-vehicle scenarios.
Simulation Mapping
In this section, we use a simulated robot-car model model to perform SLAM and visualize the robot’s motion and map-building effects in Gazebo and rviz.
- SLAM algorithm: Runs on the SpacemiT RISC-V board.
- Simulated robot model, Gazebo environment, rviz visualization: Run on a PC connected to the same network as the board.
The SpaceMiT board provides one-click launchers for three SLAM algorithms for you to choose
- slam_gmapping
- slam_toolbox
- cartographer
Comparison of the three SLAM algorithms:
| Comparison Item | slam_gmapping | slam_toolbox | cartographer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mapping accuracy | Medium | High | High |
| Graph optimization / loop closure | None | Yes | Yes |
| Relocalization support | No | Yes | Yes |
| Resource usage | Low | Medium | High |
| Map size suitability | Small | Medium | Large |
| Applicable robot size | Small | Medium/Large | Medium/Large |
| Accumulated error | High | Low | Low |
Preparation
- Flash the SpacemiT board with the Bianbu ROS system image.
- On the PC, install ROS 2 Humble and Bianbu Robot SDK.
Usage Guide
Launch the Simulation Environment
On the PC, open a terminal (Terminal 1) to install the robot model and Gazebo packages:
sudo apt install ros-humble-gazebo*
sudo apt install ros-humble-turtlebot3
sudo apt install ros-humble-turtlebot3-gazebo
sudo apt install ros-humble-turtlebot3-bringup
sudo apt install ros-humble-turtlebot3-simulations
After installation, run the following command to load the robot model and start the Gazebo simulation environment:
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
source /usr/share/gazebo/setup.sh
export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=burger
ros2 launch turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_world.launch.py
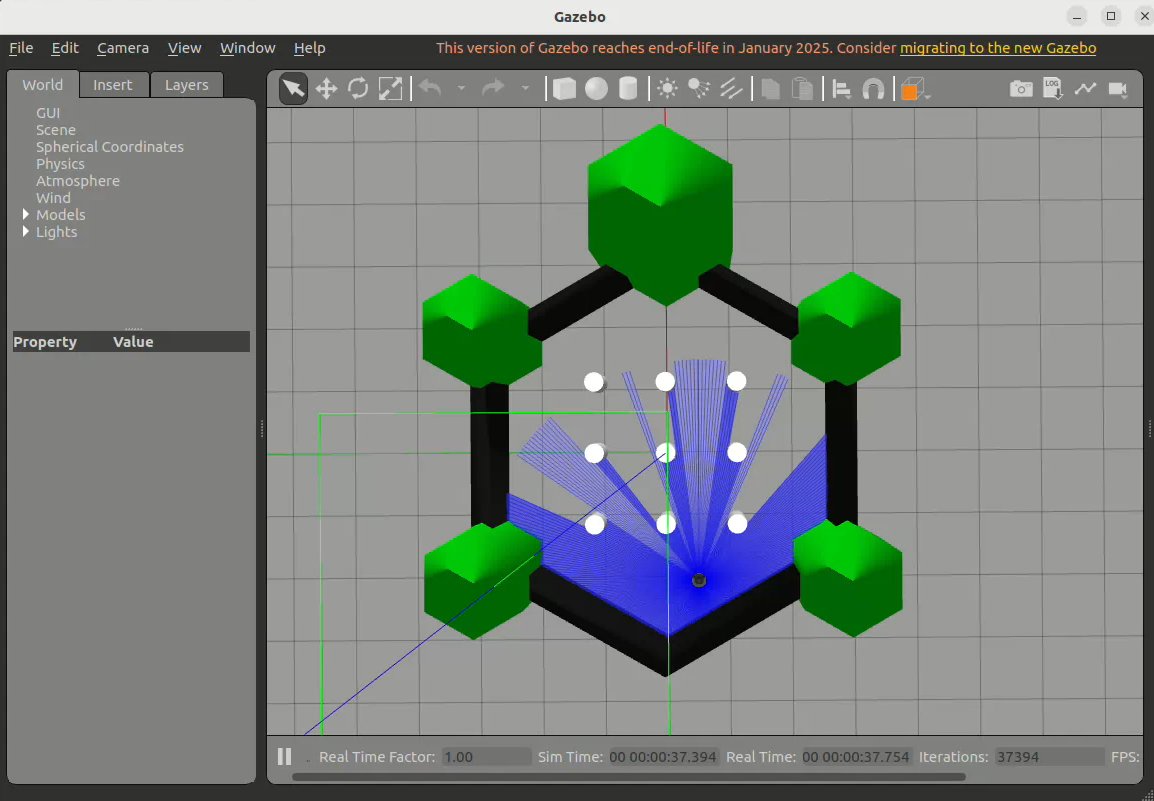
Once successfully launched, the simulation environment will appear as shown below:
On the PC, Launch rviz for visualization in another terminal (Terminal 2):
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch turtlebot3_bringup rviz2.launch.py
rviz2
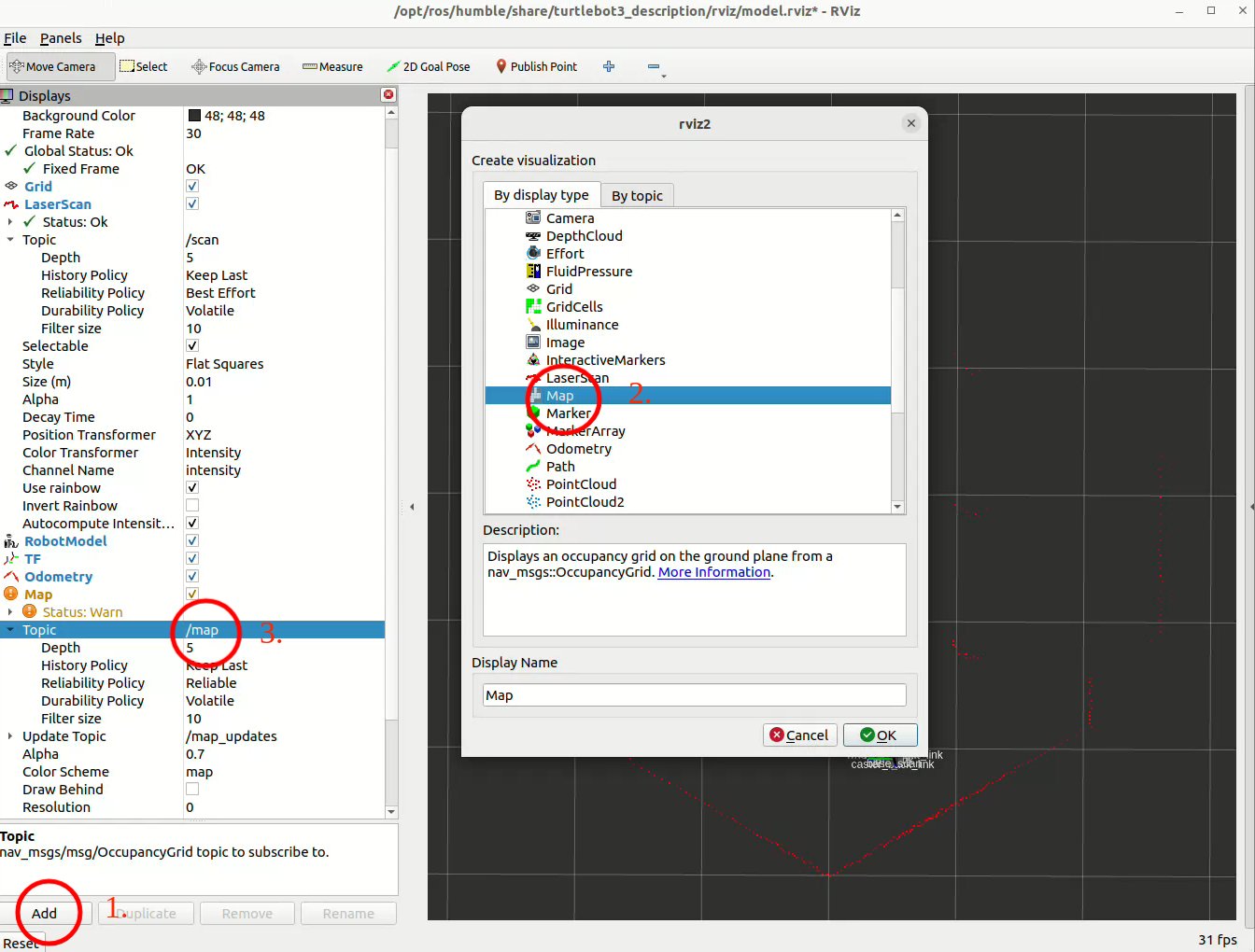
In rviz (as figure below): click Add → Map, then set the topic to /map:
Once the robot simulation environment is up, pick any one of these three SLAM algorithms on the SpacemiT board to start mapping.
Launch commands for each algorithm are provided next.
Mapping with slam_gmapping
gmapping is a 2-D SLAM algorithm based on a Particle Filter.
It uses LiDAR data to build a map in an unknown environment while estimating the robot’s pose.
GitHub: ros-perception/slam_gmapping
The slam_gmapping algorithm is pre-installed on the SpacemiT board.
Open a terminal on the SpacemiT board and run the following command to start mapping:
source /opt/bros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch br_localization slam_gmapping_sim.launch.py
Mapping with slam_toolbox
slam_toolbox is a ROS 2 toolkit for 2-D simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM).
It is designed for real-time mapping, offline refinement, loop-closure detection, and persistent map management.
GitHub: SteveMacenski/slam_toolbox
On the SpacemiT board, open a terminal and install slam_toolbox with:
sudo apt install ros-humble-slam-toolbox
To start SLAM mapping using slam_toolbox:
source /opt/bros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch br_localization slam_toolbox_sim.launch.py
Mapping with Cartographer
Cartographer is an open-source system from Google that provides real-time simultaneous localization and mapping in 2D and 3D across multiple platforms and sensor configurations.
GitHub repository: https://github.com/cartographer-project/cartographer
To install the Cartographer algorithm on SpacemiT boards:
sudo apt install ros-humble-cartographer
sudo apt install ros-humble-cartographer-ros
To launch Cartographer for mapping:
source /opt/bros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch br_localization slam_cartographer_sim.launch.py
PC-Side Visualization
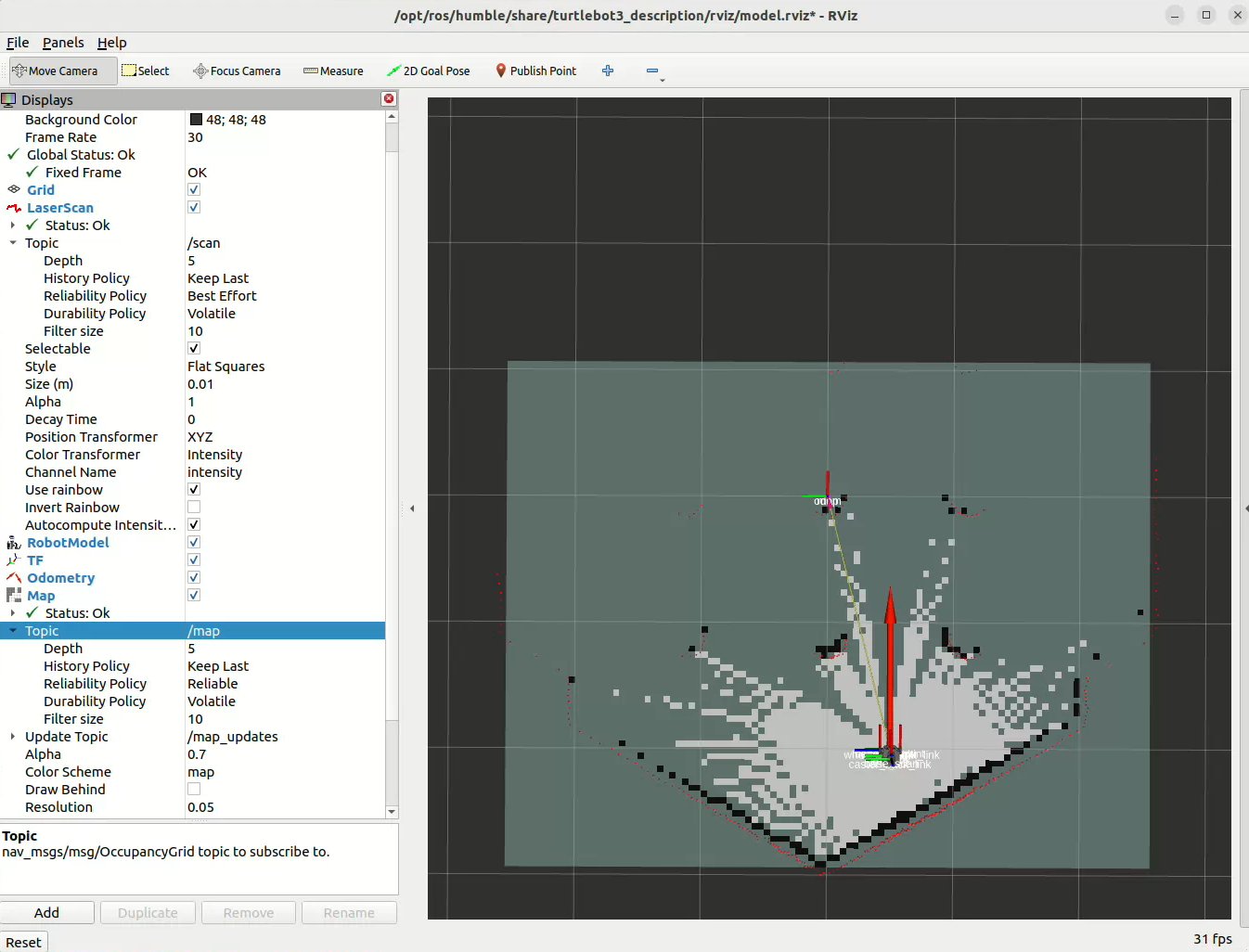
After starting SLAM mapping with any of the algorithms above, open rviz on the PC. You will see the initial map:
Next, open a new terminal on the PC and run the keyboard-control node:
sudo apt install ros-humble-teleop-twist-keyboard
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard
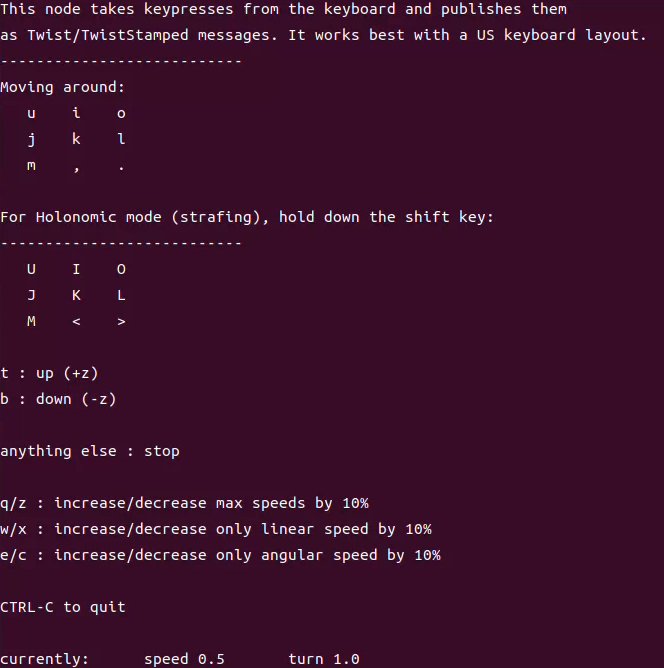
Use the keys u i o j k l m , . to drive the robot. You can watch the map being built in real time in rviz:
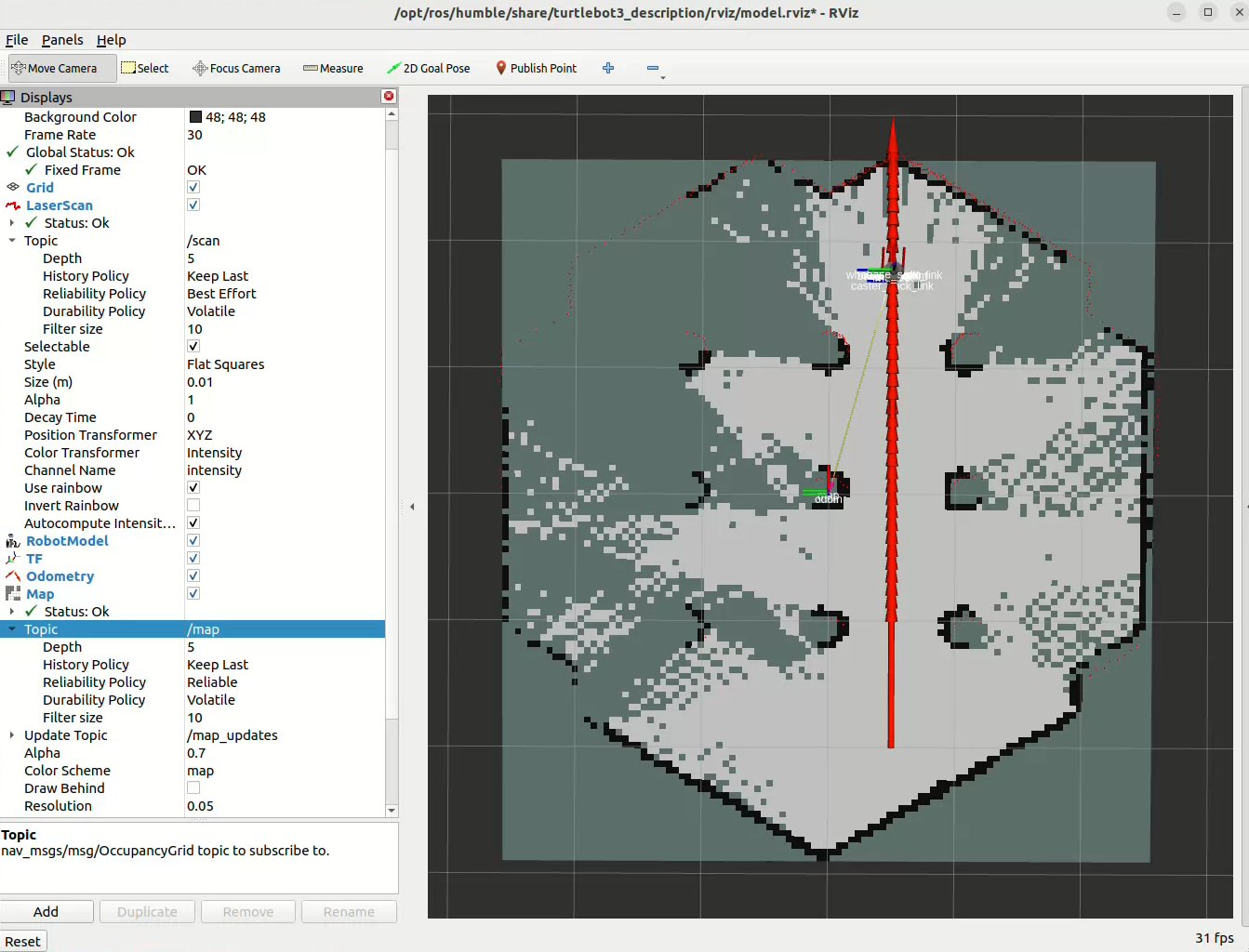
Real-Vehicle Mapping
This section demonstrates SLAM on a physical robot equipped with a SpacemiT RISC-V board, while visualizing the map in rviz on the PC.
Preparation
- Flash the SpacemiT board with the Bianbu ROS image a.
- Install ROS 2 Humble and Bianbu Robot SDK on the PC.
Usage
Run the commands below to load the real-vehicle robot parameter file and launch the desired SLAM algorithm.
Mapping with slam_gmapping
source /opt/bros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch br_localization slam_gmapping.launch.py
Mapping with slam_toolbox
source /opt/bros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch br_localization slam_toolbox.launch.py
Mapping with cartographer
source /opt/bros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 launch br_localization slam_cartographer.launch.py
PC-Side Visualization
After launching SLAM with any of the above algorithms, open a new terminal (Terminal 1) on the PC and run the keyboard-control node:
sudo apt install ros-humble-teleop-twist-keyboard
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard
Open another terminal (Terminal 2) and run the following command to start rviz.
Use the keyboard node to drive the robot and watch the mapping progress in rviz in real time:
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
source ~/ros2_demo_ws/install/setup.bash
ros2 launch br_visualization display_slam.launch.py
Save the Map
After mapping is complete, open a terminal on the SpacemiT board and run the following command to save the generated environment map into the br_navigation/map directory:
sudo apt install ros-humble-nav2-map-server
cd ~/opt/bros/humble/share/br_navigation/map
source /opt/bros/humble/setup.bash
ros2 run nav2_map_server map_saver_cli -t map -f spacemit_map1
After the command completes successfully, you will obtain the following two files:
.
├── spacemit_map1.pgm
└── spacemit_map1.yaml
0 directories, 2 files
spacemit_map1.pgm: the map image filespacemit_map1.yaml: the corresponding map configuration file.
Using SLAM, we have generated the environment map required for robot navigation. Next, you can configure Navigation2 to perform autonomous navigation.